Are you curious about how huge amounts of information get processed so quickly and accurately? Understanding the main components of electronic data processing can help you see the magic behind the scenes.
Whether you’re managing business data or just want to know how computers handle information, knowing these key parts is essential. This article will break down each component in simple terms, so you can grasp how your data moves, transforms, and gets stored.
Keep reading—you’ll discover how these pieces work together to make data processing smooth and reliable.
Core Elements Of Electronic Data Processing
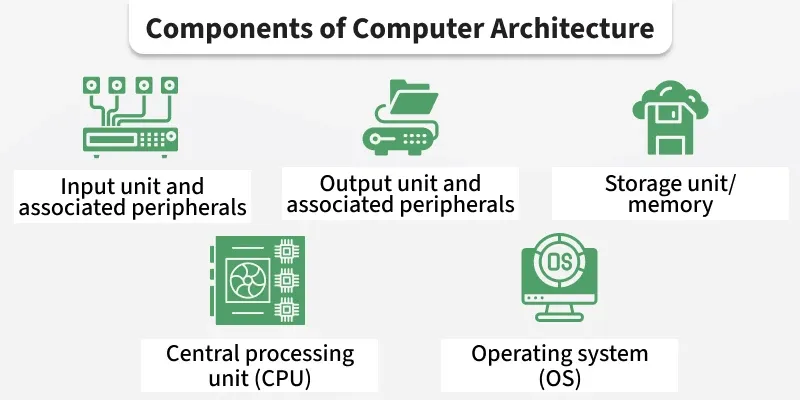
Electronic data processing relies on key components like input devices, processing units, storage, and output devices. These elements work together to collect, process, store, and display data efficiently. Understanding these parts helps grasp how data is managed electronically.
Understanding the core elements of Electronic Data Processing (EDP) is essential for anyone looking to harness the power of technology in managing information efficiently. These elements form the backbone of how data is collected, processed, and analyzed to make informed decisions. By examining these components, you can better appreciate how EDP can enhance productivity and accuracy in various applications.Data Collection
Data collection is the first step in EDP, where raw data is gathered from different sources. This could be anything from user input on a website to transaction records in a database. The quality of data collected directly impacts the effectiveness of the entire processing cycle.Data Input
Once data is collected, it needs to be inputted into a system. This process often involves converting raw data into a format that can be easily processed by computers. Ensuring accuracy during data input is crucial to prevent errors in later stages.Data Processing
Data processing is where the magic happens. This involves transforming raw data into meaningful information using algorithms and computational methods. Think about how quickly you can sort through thousands of entries and find exactly what you need.Data Storage
Processed data needs to be stored securely for future access and analysis. This component involves organizing data in databases or data warehouses. Efficient storage solutions ensure data is easily retrievable and protected from unauthorized access.Data Output
The final processed information must be presented in a user-friendly format. Data output can take various forms, such as reports, charts, or dashboards. How you present data can influence decision-making processes significantly.Data Control
Maintaining data integrity and security is paramount. Data control involves implementing measures to ensure data accuracy and safeguarding it against unauthorized changes. This element is crucial for building trust in data-driven environments. Understanding these core elements can profoundly impact how you use electronic data processing to its fullest potential. Are there ways in which you could refine your data processes to gain better insights?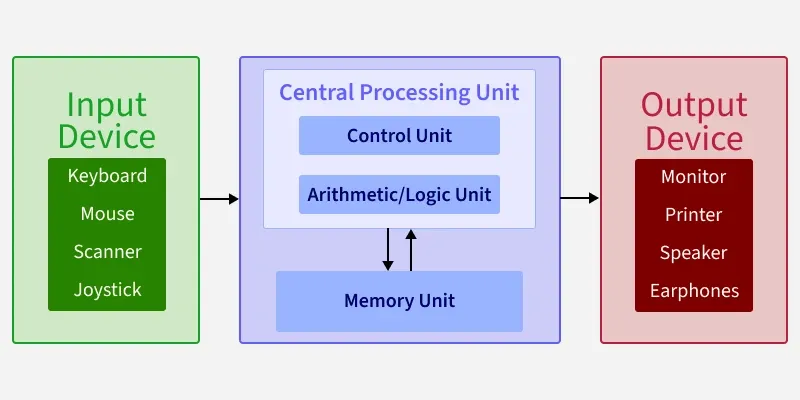
Credit: www.geeksforgeeks.org
Input Devices And Their Roles
Input devices play a vital role in electronic data processing. They serve as the bridge between the user and the computer system. These devices capture raw data from the outside world and convert it into a form the computer can understand. Without input devices, data processing would be impossible. They enable smooth and accurate data entry, which is essential for effective processing.
Types Of Input Devices
- Keyboard:Used to enter text and commands through keys.
- Mouse:Controls the pointer on the screen for selection and navigation.
- Scanner:Converts physical documents into digital images.
- Microphone:Captures sound for audio data input.
- Touchscreen:Allows direct interaction by touching the display.
- Barcode Reader:Reads barcode information for quick data entry.
- Camera:Captures images and videos as input data.
Data Collection Methods
Data collection starts with choosing the right input device. Different methods fit different needs. Manual entry uses keyboards or touchscreens for direct input. Automated collection uses devices like barcode readers and scanners to speed up data capture.
Some systems use sensors to gather data without human help. Examples include temperature sensors and motion detectors. These devices send data directly to the computer for processing.
Choosing the correct input device and method ensures faster and accurate data entry. This reduces errors and improves the quality of processed data.
Processing Units In Edp
Processing units are the heart of Electronic Data Processing (EDP). They carry out all the instructions and handle the data that flows through a system. Understanding these units helps you see how data transforms into meaningful information.
Central Processing Unit (cpu)
The CPU is often called the brain of the computer. It performs calculations and controls the flow of data within the system.
Think of it as the decision-maker that executes instructions from programs. Without a fast and efficient CPU, your data processing speed would slow down dramatically. Have you noticed how your computer lags when running multiple applications? That’s often the CPU struggling to keep up.
Memory And Storage Systems
Memory and storage are where your data lives temporarily and permanently. Memory (RAM) stores data that the CPU needs right now, making it quick to access.
Storage systems, like hard drives or SSDs, hold data long-term. Imagine trying to work on a document without saving it; you’d lose your progress instantly. These systems ensure your data is safe and ready when you need it. How often do you back up your data? Skipping this step can cause serious trouble.
Credit: utkarsh-blogs.medium.com
Output Devices And Displays
Output devices and displays are vital in electronic data processing because they transform raw data into information you can see and use. They serve as the bridge between the computer and the user, making sense of complex data through visual or printed formats.
Have you ever noticed how the clarity of your monitor or the quality of your printed reports affects your ability to understand information quickly? This is why choosing the right output devices matters for efficiency and accuracy.
Monitors And Printers
Monitors display processed data visually, allowing you to interact with information instantly. Whether you’re analyzing a spreadsheet or watching a video, the resolution and size of your monitor impact your experience.
Printers convert digital data into physical form, making documents and reports tangible. Different printers serve different needs—laser printers for sharp text and inkjets for colorful images.
- Monitors:LCD, LED, touchscreen, curved, and ultra-wide options cater to various tasks.
- Printers:Options include laser, inkjet, and dot matrix, each with pros and cons depending on speed and quality requirements.
Think about how often you rely on printed documents versus digital displays. Your choice impacts workflow, costs, and sustainability.
Report Generation
Report generation turns processed data into structured, readable formats you can share and analyze. Output devices play a key role by delivering these reports either on-screen or in print.
Good report generation tools allow customization, helping you highlight what’s important. This saves time and reduces errors by presenting data clearly.
- Automated reports save you from manual data compilation.
- Visual elements like charts and graphs improve comprehension.
- Export options let you share reports in various formats (PDF, Excel, etc.).
How do you prefer to review your reports—on a screen or on paper? Your habits can influence the type of output devices and report formats that best support your work.
Storage Components
Storage components play a vital role in electronic data processing. They hold data and instructions for computers to use. Without storage, computers cannot keep or access information effectively. These components vary in speed, capacity, and purpose.
Storage devices ensure data is saved either temporarily or permanently. The choice of storage affects system performance and usability. Understanding different storage types helps in selecting the right solution for specific needs.
Primary Vs Secondary Storage
Primary storage is the computer’s main memory. It stores data and programs currently in use. This type includes RAM (Random Access Memory) and cache memory. Primary storage is fast but usually has limited capacity. It loses data when power is off.
Secondary storage holds data permanently. Examples include hard drives, SSDs, and optical discs. It has a larger capacity than primary storage but is slower. Secondary storage keeps data even when the device is turned off. It is essential for long-term data storage and backups.
Data Retrieval Techniques
Data retrieval methods help access stored information efficiently. The technique depends on the storage type and data organization. Common methods include:
- Sequential Access – Data is read in order, one piece at a time. Used in magnetic tapes.
- Direct Access – Data is accessed directly at any location. Common in hard drives and SSDs.
- Indexed Access – Uses an index to locate data quickly. Found in databases and file systems.
Efficient data retrieval reduces wait times and improves system speed. Choosing the right technique depends on the application and storage device.
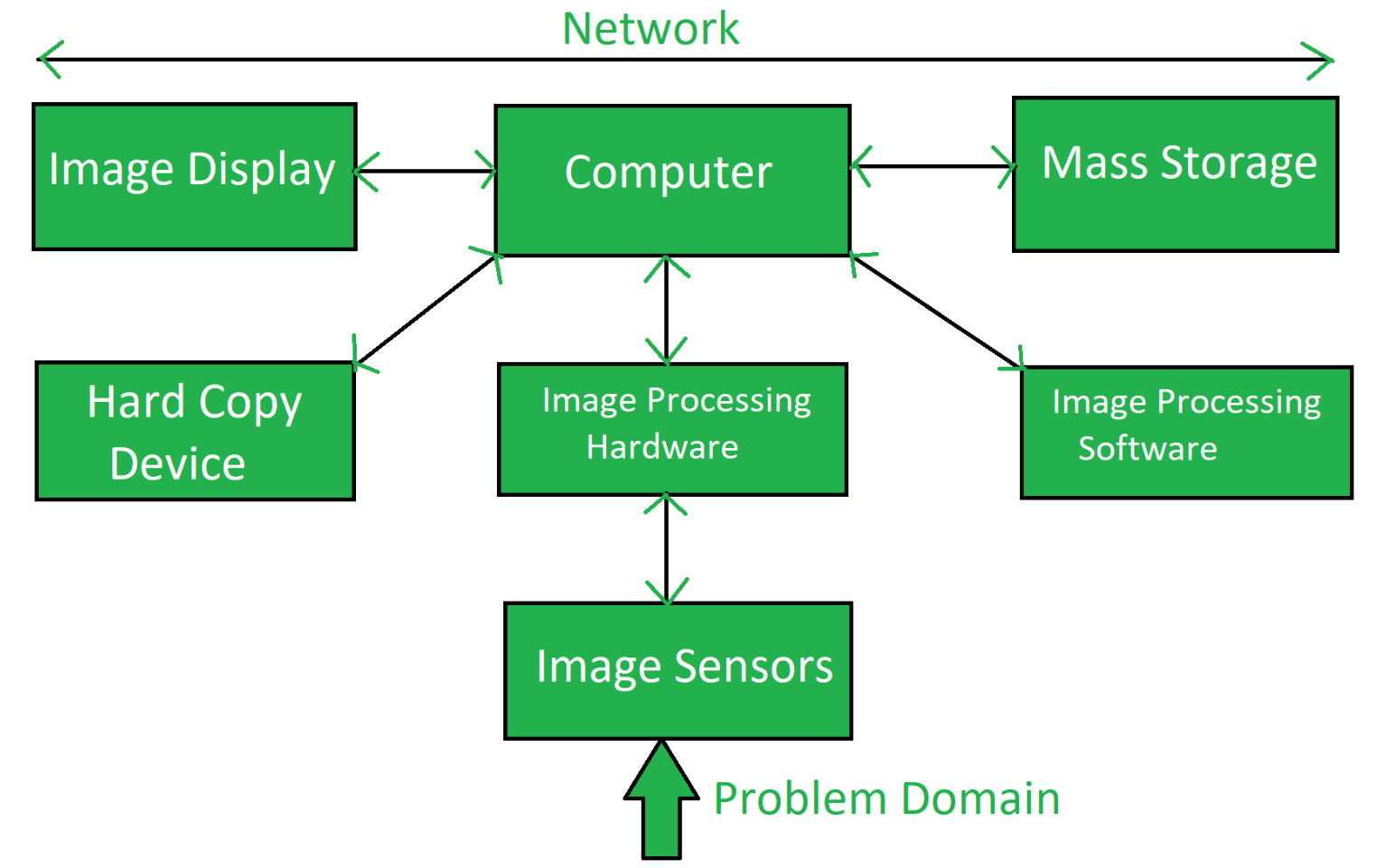
Communication And Networking
Communication and networking form the backbone of electronic data processing. Without effective communication channels, data cannot flow smoothly between devices, systems, or users. Understanding how data moves and how devices connect is crucial for anyone managing or designing data processing systems.
Data Transmission
Data transmission is the process of sending data from one point to another. This can happen over wired or wireless connections, depending on the setup. Think about your daily use of the internet—every webpage you load involves countless data transmissions happening in milliseconds.
You might wonder, what affects the speed and reliability of data transmission? Factors like bandwidth, signal strength, and the type of transmission medium (fiber optic cables, Wi-Fi, or copper wires) play a big role. If you’ve ever experienced slow internet or dropped calls, you’ve encountered transmission issues firsthand.
Network Interfaces
Network interfaces are the hardware and software components that allow devices to connect and communicate on a network. Examples include network interface cards (NICs) in computers and wireless adapters in smartphones. These interfaces translate data into signals that can travel across the network.
Choosing the right network interface can impact your data processing setup significantly. For example, a high-speed Ethernet card can dramatically improve data transfer rates in an office environment. What type of network interface does your device use, and how might upgrading it enhance your overall system performance?
Software In Electronic Data Processing
Software plays a key role in electronic data processing. It controls how data is handled, stored, and analyzed. Software ensures machines work efficiently and tasks are completed accurately. There are two main types of software in electronic data processing: system software and application software.
System Software
System software acts as the foundation for all other software. It manages hardware and basic system operations. Examples include operating systems, device drivers, and utility programs. This software helps computers run smoothly and supports application software. Without system software, hardware and applications cannot work together.
Application Software
Application software is designed for specific tasks. It processes data and produces useful information. Examples include word processors, database programs, and spreadsheet tools. This software helps users perform jobs like creating documents or analyzing data. Application software depends on system software to function properly.
Security In Data Processing
Security in data processing is a critical element that protects sensitive information from unauthorized access and potential breaches. Without strong security measures, the integrity and confidentiality of your data can be easily compromised. Ensuring robust security safeguards not only builds trust but also prevents costly data loss or theft.
Access Controls
Access controls determine who can view or use data during processing. You should set clear permissions based on roles to limit data access strictly to authorized users.
Think about your own experience: have you ever been frustrated by accessing a system only to find you lack the rights to perform needed actions? Proper access controls prevent such issues while keeping your data safe.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):Assigns permissions based on user roles like admin, user, or guest.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):Adds extra verification layers to confirm user identity.
- Audit Logs:Track who accessed data and when, helping detect suspicious activity.
Data Encryption
Data encryption converts information into a coded format that only authorized parties can decode. This protects your data even if someone intercepts it during processing or transmission.
Imagine sending a private letter through the mail. Encryption is like putting that letter in a locked box—only the recipient has the key.
- At-Rest Encryption:Safeguards stored data on servers or devices.
- In-Transit Encryption:Protects data moving across networks using protocols like TLS.
- End-to-End Encryption:Ensures data is encrypted throughout its entire journey.
How confident are you that your current data processing methods keep your information secure? Taking steps to strengthen access controls and encryption can make a big difference in protecting your valuable data.
Credit: www.geeksforgeeks.org
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Electronic Data Processing (edp)?
Electronic Data Processing (EDP) is the automated method of collecting, processing, and storing data using computers. It enhances accuracy, speed, and efficiency in handling large volumes of information for businesses and organizations.
What Are The Key Components Of Edp Systems?
Key components of EDP systems include hardware, software, data, procedures, and personnel. Hardware processes data, software controls operations, data is input information, procedures guide tasks, and personnel manage the system.
How Does Hardware Contribute To Electronic Data Processing?
Hardware in EDP refers to physical devices like computers, storage units, and input/output devices. It performs data input, processing, storage, and output functions essential to the entire data processing cycle.
Why Is Software Important In Edp?
Software controls and manages data processing tasks in EDP. It includes programs and applications that organize, analyze, and convert raw data into meaningful information efficiently.
Conclusion
Electronic Data Processing depends on key parts working well together. These parts include input devices, processing units, storage, and output devices. Each has a clear role in handling data quickly and accurately. Understanding these components helps in managing data better.
It also supports smoother business operations and decision-making. Knowing how these elements connect makes technology easier to use. Keep these basics in mind to appreciate how data processing works daily. Simple, clear steps lead to effective data handling.

Leave a Reply