Have you ever wondered how the software or systems you use every day actually come to life and keep running smoothly? Understanding system implementation and maintenance is key to making sure your business tools work exactly when you need them.
This process isn’t just about setting things up once; it’s about keeping your systems reliable, efficient, and ready for whatever challenges come next. If you want to learn how to make your technology investments truly pay off, keep reading. You’ll discover the essential steps and tips that can save you time, money, and headaches down the line.
System Implementation Process
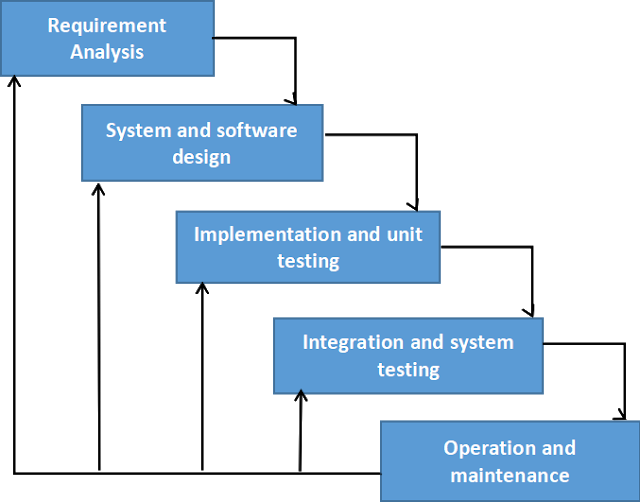
The system implementation process is the backbone of turning ideas and plans into a fully functioning system that meets your needs. It involves several key stages where careful attention ensures that the system performs reliably and efficiently. Each phase builds on the previous one, shaping your system’s success.
Planning And Preparation
Planning sets the stage for everything that follows. You define clear goals, gather requirements, and allocate resources. Without thorough preparation, unexpected problems can arise that delay your project and increase costs.
During this phase, consider who will use the system and what their needs are. Have you identified potential risks? Preparing a roadmap keeps your team aligned and ready for challenges.
Design And Development
This phase transforms your plans into blueprints and actual code. Designers create the system architecture, while developers write the software to meet those designs. Attention to detail here prevents headaches later.
Think about user experience and system scalability. Have you ensured the design is flexible enough for future changes? Solid development practices and clear documentation make maintenance easier down the line.
Testing And Quality Assurance
Testing checks if your system works as expected. It catches bugs and performance issues before users encounter them. Skipping or rushing this step can lead to costly fixes after deployment.
Include different types of testing like functional, load, and security tests. Ask yourself: Does the system handle real-world scenarios effectively? Quality assurance protects your investment and builds user trust.
Deployment And Integration
Deployment moves your system from development into the live environment. Integration ensures it works smoothly with existing tools and processes. This phase requires careful coordination to avoid disruptions.
Are you prepared for a rollback if something goes wrong? Communicate clearly with your users to manage expectations. Successful deployment is about more than just launching—it’s about seamless transition and ongoing support.
Credit: www.charterglobal.com
Challenges In System Implementation
Implementing a new system is rarely straightforward. You will face various challenges that can slow down progress or even derail the entire project. Understanding these hurdles helps you prepare better and avoid common pitfalls.
Resource Allocation
Allocating the right resources at the right time is often tougher than it sounds. You might have limited budget, tight deadlines, or a small team juggling multiple tasks.
For example, I once worked on a system rollout where key developers were pulled away for urgent fixes elsewhere. This delay taught me the importance of prioritizing and securing dedicated resources early on.
Ask yourself: Do you have enough skilled people assigned, and are they fully available for the project?
Change Management
People resist change, especially when it disrupts their daily work. Managing this resistance is critical to successful implementation.
Communicating the benefits clearly and involving users early can ease the transition. Without this, you risk low morale and active pushback.
Think about how you can create champions within your team who will support and promote the new system.
User Training And Adoption
Even the best system fails if users don’t know how to use it. Training is not just a one-time event but an ongoing process.
When I led a training program, I realized that hands-on sessions worked better than just manuals or videos. People remember what they practice.
Consider the different learning styles of your users and offer multiple training formats to increase adoption.
Technical Issues And Bugs
No system is perfect out of the box. Bugs and technical issues will appear and must be handled promptly.
Having a clear process for reporting and fixing problems helps maintain trust in the system. It’s frustrating for users when issues linger unresolved.
Prepare your team to expect and quickly respond to these hiccups so the implementation doesn’t lose momentum.
Strategies For Successful Implementation
Successful system implementation requires clear plans and strong strategies. The right approach reduces risks and improves user acceptance. Focus on communication, involvement, training, and ongoing support for best results.
Effective Communication
Clear communication keeps everyone informed and aligned. Share updates regularly with simple language. Use multiple channels like emails, meetings, and newsletters. Avoid jargon to ensure all team members understand the message.
Encourage questions and feedback to prevent misunderstandings. Transparency builds trust and smooths the implementation process.
Stakeholder Involvement
Engage stakeholders early and often. Their input helps shape system requirements and features. Involve users, managers, and IT staff in discussions. This creates a sense of ownership and support.
Address concerns quickly to avoid resistance. Active participation leads to smoother adoption and fewer surprises.
Comprehensive Training Programs
Provide clear, hands-on training for all users. Use simple materials like videos, guides, and workshops. Tailor training to different skill levels and roles.
Allow time for practice and questions. Good training increases confidence and reduces errors after launch.
Continuous Monitoring And Feedback
Track system performance and user experience regularly. Use surveys, helpdesk reports, and usage data. Identify issues early and fix them fast.
Encourage ongoing feedback from users. This helps improve the system and keeps it relevant to business needs.
System Maintenance Essentials
System maintenance is a key part of keeping technology running smoothly. It involves tasks that ensure systems stay updated, secure, and efficient. Regular care prevents problems and extends the life of the system.
Maintenance covers various areas, from updating software to monitoring performance. Each part plays a role in avoiding downtime and data loss. Understanding these essentials helps maintain a stable and reliable system.
Regular Updates And Upgrades
Updates fix bugs and improve system functions. Upgrades add new features and improve compatibility. Scheduling these regularly keeps the system current and reduces errors. Ignoring updates can lead to slow performance and security risks.
Performance Monitoring
Tracking system performance helps spot issues early. Use tools to watch CPU, memory, and network usage. Identify slowdowns or failures before they affect users. Performance checks keep systems running at their best.
Security Management
Security protects systems from threats and attacks. This includes installing patches, managing user access, and scanning for malware. Strong security reduces the chance of data breaches and loss. Regular reviews keep security measures effective.
Backup And Recovery Procedures
Backing up data prevents loss during failures or attacks. Recovery plans restore systems quickly after problems. Test backups often to ensure data is safe and accessible. Reliable backup and recovery reduce downtime and data damage.
Types Of System Maintenance
Understanding the different types of system maintenance helps you manage your software or hardware more effectively. Each type targets specific issues or improvements, ensuring your system stays reliable and efficient. Knowing these can save you time and reduce unexpected downtime.
Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance focuses on fixing problems after they occur. Think of it as troubleshooting bugs or errors that disrupt your system’s normal operation. If your app crashes or a feature stops working, this type of maintenance is what gets things back on track.
Have you ever experienced a sudden software glitch that halted your work? Corrective maintenance is your immediate response, restoring functionality and preventing further damage.
Adaptive Maintenance
Systems need to keep pace with changes in their environment. Adaptive maintenance modifies your system to work with new operating systems, hardware, or business rules. It’s about staying compatible and relevant as external conditions evolve.
For example, when a new version of a database software is released, adaptive maintenance ensures your application still connects smoothly. Without it, your system could become outdated or unusable.
Perfective Maintenance
This type is all about improving your system’s performance and usability. Perfective maintenance adds new features or enhances existing ones based on user feedback. It’s how your system grows better over time, not just fixing issues but becoming more valuable.
Imagine you receive suggestions from your team to speed up a report generation or simplify a dashboard. Implementing those changes falls under perfective maintenance, making your system more efficient and user-friendly.
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance aims to stop problems before they happen. It includes activities like code refactoring, updating security patches, and cleaning up unused components. This proactive approach helps reduce system failures and extends its lifespan.
Have you ever postponed an update only to face bigger issues later? Preventive maintenance asks you to act early, keeping your system stable and secure over time.

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Best Practices For System Maintenance
Maintaining a system effectively requires more than just fixing issues as they arise. It demands a strategic approach that keeps your system running smoothly and adapts to evolving needs. Focusing on best practices for system maintenance helps you avoid downtime and enhances user satisfaction.
Proactive Problem Solving
Waiting for problems to appear can cost you time and money. Instead, regularly monitor your system’s performance to spot potential issues early.
Set up automated alerts for unusual activity or errors. This way, you can address problems before they escalate and disrupt your operations.
Ask yourself: What small signs might indicate a bigger issue? Catching these early can save you headaches later.
Documentation And Record Keeping
Keeping detailed records of changes, updates, and issues is crucial. Good documentation helps you track what has been done and why.
It also makes onboarding new team members easier and ensures consistency in maintenance tasks. Use clear and simple language to make your documentation accessible to everyone.
Have you ever struggled to fix a recurring problem because you lacked proper notes? Avoid that by logging everything meticulously.
User Feedback And Improvement
Your users are the best source of insight into how well the system performs daily. Encourage them to share feedback regularly.
Use surveys, direct interviews, or feedback forms to gather their input. Then, prioritize improvements based on their experiences and suggestions.
Think about what your users need most and focus your maintenance efforts there. What small change could make their work much easier?
Collaboration With It Teams
Maintenance isn’t a solo task. Work closely with IT professionals who understand the technical details and can offer expert solutions.
Regular meetings and clear communication channels ensure everyone stays informed about system status and upcoming updates.
Have you set up a routine check-in with your IT team? These conversations can uncover hidden issues and spark innovative ideas.
Credit: genius-learner.medium.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is System Implementation In It?
System implementation is the process of installing and configuring new software or hardware. It ensures that the system works as intended. This phase includes testing, training, and deployment to integrate the system into daily operations smoothly.
Why Is System Maintenance Important?
System maintenance keeps software and hardware running efficiently. It fixes bugs, updates features, and improves security. Regular maintenance prevents system failures and extends the system’s life, ensuring consistent performance.
What Are The Key Phases Of System Implementation?
Key phases include planning, installation, configuration, testing, training, and deployment. Each step ensures the system meets user requirements and works without errors. Proper execution reduces risks and enhances user satisfaction.
How Does System Maintenance Improve Performance?
Maintenance optimizes system speed and reliability by fixing issues and applying updates. It prevents downtime and data loss. Regular checks and improvements keep systems aligned with evolving business needs.
Conclusion
System implementation and maintenance keep technology running smoothly. They help businesses work better and avoid problems. Good planning and regular updates save time and money. Teams must watch systems closely and fix issues fast. This process supports growth and adapts to changes.
Understanding these steps makes technology less confusing. It ensures the system stays useful and reliable. Simple care keeps everything on track. A strong system helps reach business goals with less stress.

Leave a Reply